Unlocking the Future of Coastal Lagoon Monitoring with the Mar Menor Case Study
In the face of mounting environmental pressures, the monitoring of coastal ecosystems has never been more crucial. Coastal lagoons, dynamic and rich in biodiversity, are particularly vulnerable to anthropogenic impacts. The Mar Menor lagoon in Murcia, Spain, stands as a poignant example of such a system under siege, primarily due to the eutrophication process spurred by excessive nutrient inputs. This backdrop sets the stage for a groundbreaking study recently published as part of the SMARTLAGOON project, titled "Assessment of oceanographic services for the monitoring of highly anthropised coastal lagoons: The Mar Menor case study". This research sheds light on the current challenges faced in...
SMARTLAGOON modeling workshop in Oslo
In March 2024, the modeling work packages convened for a two-day session in Oslo hosted by NIVA to explore the integration of socio-economic and environmental models—this effort aimed to enhance understanding of the connections between human activities and natural systems. The meeting brought together the socio-economic system dynamics (SD) model with the catchment model (SWAT) and the lagoon model (GOTM) to brainstorm strategies for integration. While socio-economic models delve into human behaviors, decision-making processes, and economic activities, environmental models simulate climate dynamics, land use changes, and ecosystem functions. Despite the challenge of creating a computational coupling, we devised alternative ways by providing boundary conditions...
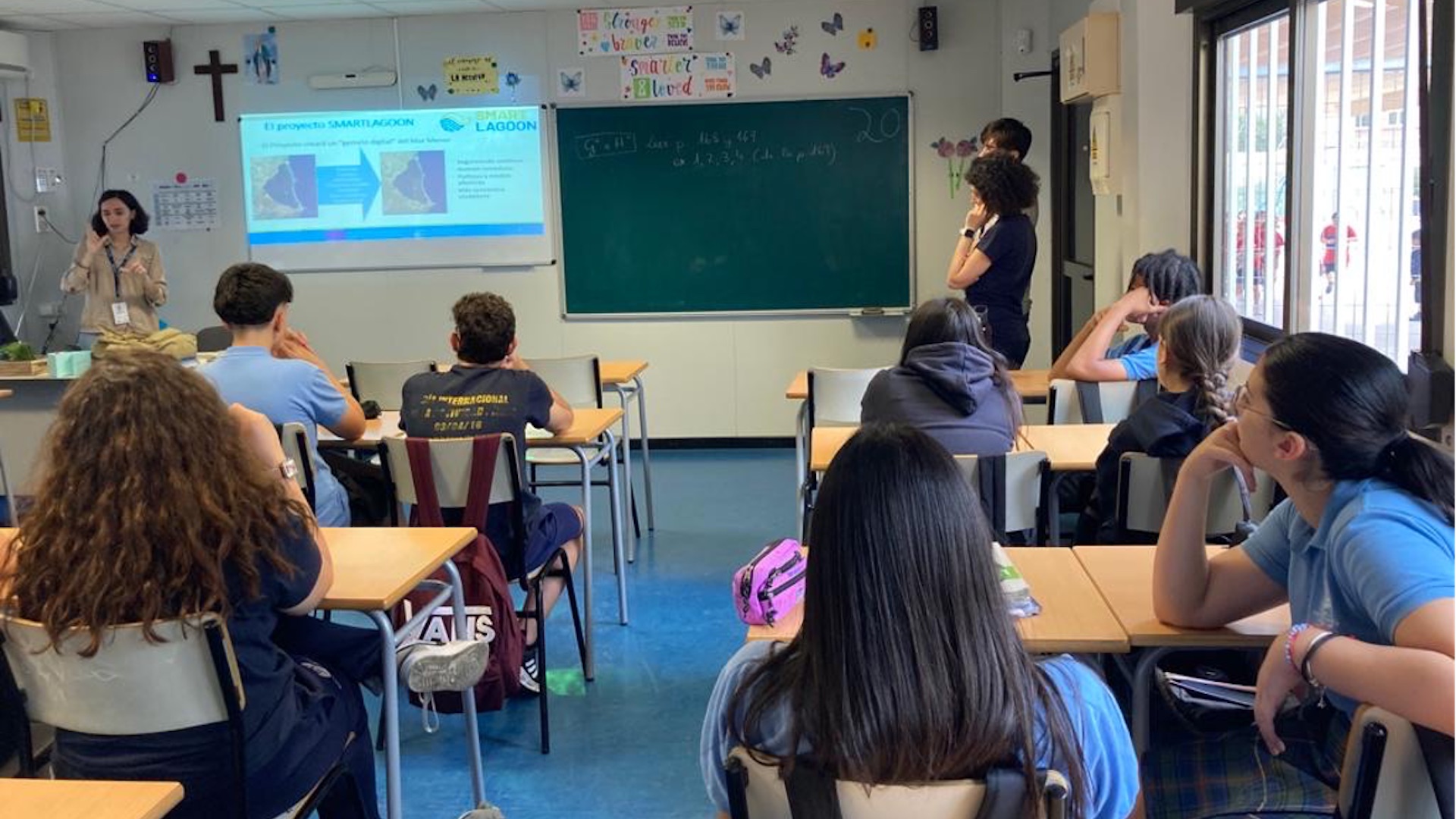
Citizen Science and co-design initiatives with students to raise awareness about SMARTLAGOON and the Mar Menor
Citizen Science is a powerful tool for engaging individuals with diverse backgrounds, skills, and ages. Numerous studies have demonstrated its successful application in educational contexts, raising awareness about specific topics and involving students in serious discussions. In this context, we utilized Citizen Science as an educational tool for teenagers. Specifically, we conducted two activities in May 2023, engaging two classes (33 + 19 students) from a high school near Murcia (CEIP San Vicente de Paul, in El Palmar). The students were 15-16 years old, and each session lasted two hours, covering: An introduction to SMARTLAGOON and the issues surrounding Mar Menor. An overview of the...
Validation of the hydrographic model of the SMARTLAGOON project in a riverbed in the Campo de Cartagena
Currently, the accurate measurement of the variables necessary for hydrological modeling faces the challenge of costly models and sensors. This problem is aggravated in basins with high water stress where monitoring is more complex. Such is the case of Campo de Cartagena, characterized by ephemeral streams and average annual rainfall of less than 300 mm. To address this situation, we implemented an innovative methodology that combines citizen science, through a mobile application that is able to obtain flow rates from recordings taken by citizens at specific control points; in addition to low-cost high-tech sensors capable of measuring the height of the water sheet, thanks to...
Coupled modelling of watersheds and water bodies – from global scale to Mar Menor
We may not always realise it, but our lives are surrounded by models. If we define a model as a “representation of something”, we can see a map as a model of real-world topography - helping us to navigate -, or a mannequin in a shop as a model of our bodies - so we can better visualise how we would look in certain clothes. Models can also be numerical: a weather forecast model tells us (not always accurately) if it is going to rain tomorrow. But also bus tables, city infrastructure, airplane design, and so many more things, are partially the product of...
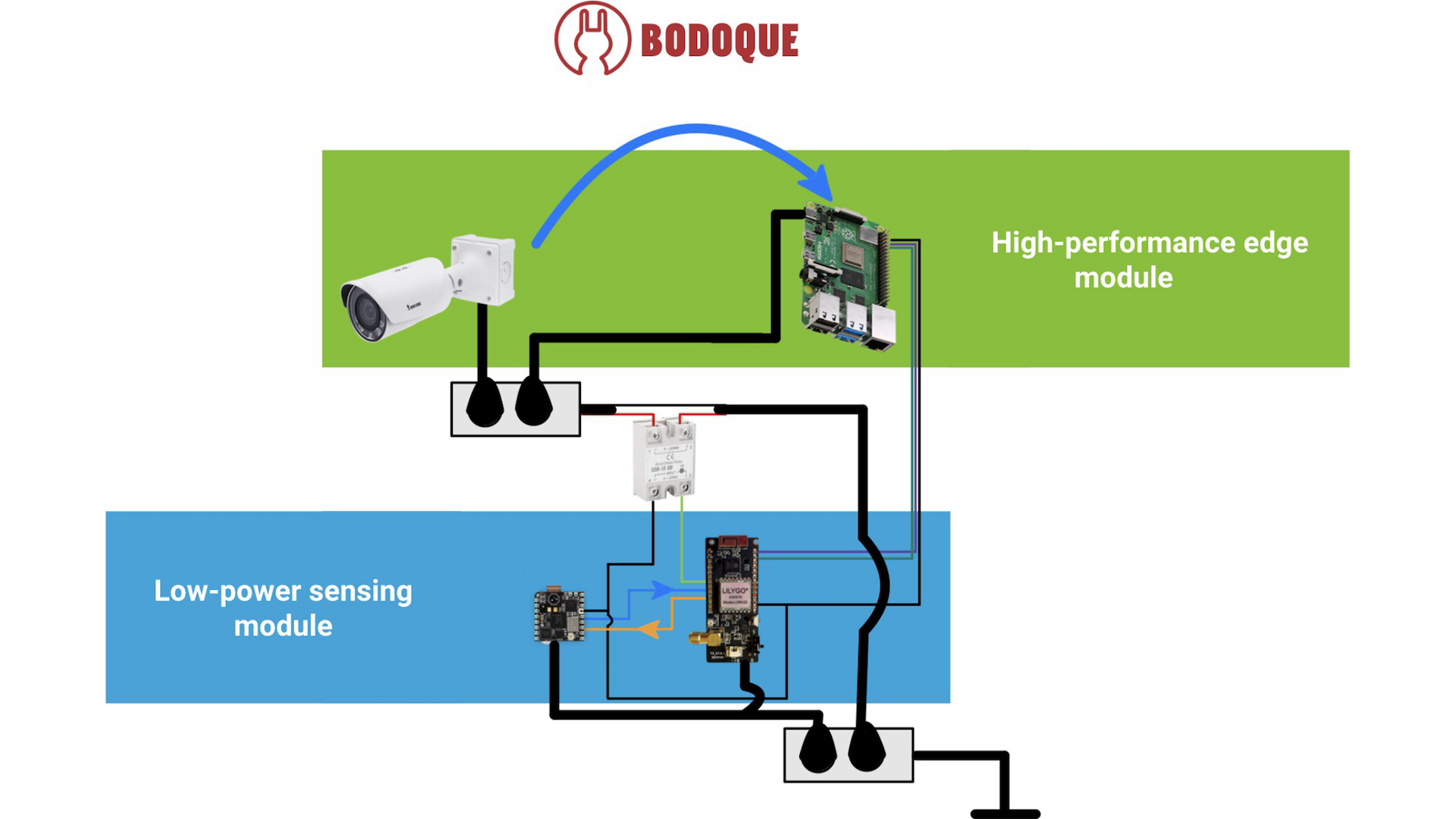
BODOQUE: An Energy-Efficient Flow Monitoring System for Ephemeral Streams
Effective environmental monitoring is crucial for managing global environmental challenges and providing the necessary data for Environmental Intelligence (EI). This discipline involves the integration of data from various sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of specific regions or processes. In this post, we introduce BODOQUE, a hardware-software infrastructure to monitor water flows in ephemeral streams where the water rarely flows with great force. BODOQUE uses a low-power TinyML-based camera to detect the presence of water, activating a more complex system to measure flow only when the water flows, thereby optimizing energy consumption. This device is being deployed in the Segura basin, Murcia, Spain. This...
Image-based turbidity measurements
The objective of the SMARTLAGOON project is to develop a digital twin of the Mar Menor and its entire watershed. It is intended to give real-time insights of the state of the Mar Menor, and also forecast the risk of hypoxia in the short-term future. The digital twin integrates water quantity and quality models and real-time sensor data. Regarding the real-time sensors, at SMARTLAGOON photrack is developing methods to measure turbidity via images. Water clarity can be used as in indicator for water quality assessment, its spatio-temporal monitoring is important for water management, and environmental protection of aquatic ecosystems. There are available sensors which can measure...
Satellite Imagery Approach in the H2020 SMARTLAGOON Project
Are you familiar with the products of the European Space Agency's (ESA) Copernicus programme? We are using both Sentinel-3 (S3) and Sentinel-2 (S2) in SMARTLAGOON because we are interested in using the almost daily remotely sensed water quality data to calibrate our Mar Menor lagoon model, which is provided by S3, but unfortunately at a very low resolution - i.e. 300 m pixels. We realised that in such a context, in a shallow water lagoon, there is a clear relationship between aerial images - such as those provided by S2 every 5-10 days and with a resolution of up to 10 m pixels - and...
Into the Depths: Exploring Mar Menor’s Virtual Counterpart
In 2019, a massive fish kill was reported from the iconic Mar Menor – likely a result of prolonged water column stratification and a long period of hypoxia (low oxygen levels) in large parts of the lagoon. Stratification, where the water column "divide" into distinct layers of density due to different temperatures or salinity, can oftentimes result in low or even completely depleted oxygen levels near the bottom. Even if these stratification events are short-lived (e.g. a few days or less), as is typical in shallow systems, such as Mar Menor, this can still be enough to cause low oxygen levels near the bottom....
SMARTLAGOON at the 2023 Denmark SWAT Conference
From June 26th to 30th, our researchers of the European project SMARTLAGOON attended the 2023 Denmark SWAT Conference. This congress held at the Aarhus University had a massive participation with more than 170 participants from 41 different countries. Under the titles "Developing a high-resolution global digital soil map for enhanced hydrological modelling with the SWAT+ model" and "Evaluating the hydrological performance of three global digital soil maps using SWAT+" the researchers Adrián López-Ballesteros and Gerardo Castellanos-Osorio presented the results obtained in the paper "DSOLMap, a novel high-resolution global digital soil property map for the SWAT + model: Development and hydrological evaluation". This research details how...